- 詳細 2014年9月15日 08:50更新
-
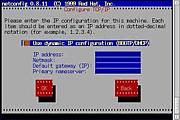
ゲートウェイは、 ノード ( ルータ上の) TCP / IP別のネットワークへのアクセスポイントとして機能するネットワーク。 A default gateway is the node on the computer network that the network software uses when an IP address does not match any other routes in the routing table . デフォルトゲートウェイは、上のノードであるコンピュータネットワーク時にネットワークソフトウェアが使用するIPアドレスが他のどのルートが一致していないルーティングテーブルを 。
In home computing configurations, an ISP often provides a physical device which both connects local hardware to the Internet and serves as a gateway.ホーム·コンピューティングの構成では、 ISPは頻繁にローカルのハードウェアを接続し、両方の物理デバイスを提供インターネットとのゲートウェイとして機能します。 Such devices include DSL modems and cable modems .このようなデバイスが含まれ、DSLモデムやケーブルモデムを 。
In organizational systems a gateway is a node that routes the traffic from a workstation to another network segment .組織のシステムでは、ゲートウェイからのトラフィックをルーティングノードであるワークステーションを別のネットワークセグメント 。 The default gateway commonly connects the internal networks and the outside network (Internet).デフォルトゲートウェイは、一般的に内部ネットワークと外部ネットワーク(インターネット)に接続します。 In such a situation, the gateway node could also act as a proxy server and a firewall .このような状況では、ゲートウェイノードでは、としても作用することができるプロキシサーバーとファイアウォール 。 The gateway is also associated with both a router , which uses headers and forwarding tables to determine where packets are sent, and a switch , which provides the actual path for the packet in and out of the gateway.ゲートウェイは、両方に関連付けられているルータヘッダおよび使用して、 転送テーブルをパケットが送信される場所を決定し、 スイッチのゲートウェイのうちで、パケットの実際のパスを提供します。
In other words, a default gateway provides an entry point and an exit point in a network.言い換えると、デフォルトゲートウェイは、エントリポイント、ネットワーク内の出口点を提供します。
Contents中身 [hide]
1 Example1 1 例1
2 Example2 2 例2
3 See also 3 も参照してください。
4 External links 4 外部リンク
[ edit ] Example1 [ 編集 ] 例1 An office network consists of six hosts and a router is given as:オフィスのネットワークは、6つのホストで構成されており、ルータは次のように与えられます。
Hosts addresses:ホストアドレス:
192.168.4.3 192.168.4.3
192.168.4.4 192.168.4.4
192.168.4.5 192.168.4.5
192.168.4.6 192.168.4.6
192.168.4.7 192.168.4.7
192.168.4.8 192.168.4.8
Router (this side) address:ルータ(こちら側)のアドレス:
192.168.4.1 192.168.4.1
The network has a subnet mask of:ネットワークが持つサブネットマスクのを:
255.255.255.0 (/24 in CIDR notation) 255.255.255.0(の/ 24 のCIDR表記)
Thus the usable network ranges from addresses 192.168.4.1 to 192.168.4.254.したがって、使用可能なネットワークがアドレス192.168.4.1から192.168.4.254の範囲である。 (TCP/IP defines the addresses 192.168.4.0 and 192.168.4.255 for special functions.) (TCP / IPは、特殊関数のアドレス192.168.4.0と192.168.4.255を定義します。)
The office's hosts will send packets addressed to IPs within this range directly, by resolving the destination IP address into a MAC address through an ARP sequence (if not already known through the host's ARP cache) and then enveloping the IP packet into a layer 2 (MAC) packet addressed to the destination host.オフィスのホストがに宛先IPアドレスを解決することによって、直接この範囲内のIPアドレス宛てのパケットを送信するMACアドレスを介してのARP (シーケンス(既にホストのARPキャッシュを介して知られていない場合)、レイヤ2にIPパケットを包むMAC)パケットが宛先ホストに宛てた。
Packets addressed outside of this range (for this example, a packet addressed to 192.168.12.3) cannot travel directly to the destination.パケットは、(この例では、パケットは192.168.12.3宛て)この範囲の外に宛て先に直接移動することはできません。 Instead they must be sent to the default gateway for further routing to their ultimate destination.代わりに、彼らはさらに、最終的な宛先にルーティングするためにデフォルトゲートウェイに送信する必要があります。 In this example, the default gateway uses the IP address 192.168.4.1, which is resolved into a MAC address with ARP in the usual way.この例では、デフォルトゲートウェイは通常の方法でARPとMACアドレスに解決されるIPアドレス192.168.4.1を使用しています。 Note that the destination IP address remains 192.168.12.3, but the next-hop physical address is that of the gateway, rather than of the ultimate destination.宛先IPアドレスが192.168.12.3のままですが、ネクストホップの物理アドレスは、ゲートウェイのではなく、最終的な宛先のことであることに注意してください。
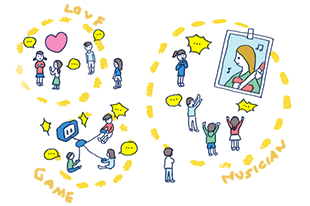
[ edit ] Example2 [ 編集 ] 例2 A network with three routers and three hosts, connected to the Internet through router1.ルータ1を介してインターネットに接続された3つのルータと3のホストを持つネットワーク。
Hosts and addresses:ホストおよびアドレス:
PC1 10.1.1.100, default gateway 10.1.1.1 PC1 10.1.1.100、デフォルトゲートウェイ10.1.1.1
PC2 172.16.1.100, default gateway 172.16.1.1 PC2 172.16.1.100、デフォルトゲートウェイ172.16.1.1
PC3 192.168.1.100, default gateway 192.168.1.96 PC3 192.168.1.100、デフォルトゲートウェイ192.168.1.96
Router1: Router1は:
Interface 1 5.5.5.2 ( public IP )インターフェイス1 5.5.5.2( パブリックIP )
Interface 2 10.1.1.1インタフェース2 10.1.1.1
Router2: Router2の:
Interface 1 10.1.1.2インタフェース1 10.1.1.2
Interface 2 172.16.1.1インタフェース2 172.16.1.1
Router3: router3によって:
Interface 1 10.1.1.3インタフェース1 10.1.1.3
Interface 2 192.168.1.96インタフェース2 192.168.1.96
Network mask in all networks: 255.255.255.0 (/24 in CIDR notation).すべてのネットワークのネットワークマスク:255.255.255.0(の/ 24 のCIDR表記)。
If the routers do not use a Routing Information Protocol to discover which network each router is connected to, then the routing table of each router must be set up.ルータは使用しない場合は、ルーティング情報プロトコルを各ルータが接続されているネットワークを検出し、次に各ルータのルーティングテーブルを設定する必要があります。
Router1 Router1に
Network IDネットワークID Network maskネットワークマスク Gatewayゲートウェイ Interface (examples; may vary)インターフェース(例;異なる場合があります) Cost (decreases the TTL )コスト(減少TTLを )
0.0.0.0 ( default route ) 0.0.0.0( デフォルトルート ) 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Assigned by ISP (eg 5.5.5.1) ISP(例えば5.5.5.1)によって割り当てられた eth0 (Ethernet 1st adapter) eth0の(イーサネットアダプタ第一) 10 10
10.1.1.0 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.1 10.1.1.1 eth1 (Ethernet 2nd adapter) eth1の(イーサネット第二アダプタ) 10 10
172.16.1.0 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.2 10.1.1.2 eth1 (Ethernet 2nd adapter) eth1の(イーサネット第二アダプタ) 10 10
192.168.1.0 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.3 10.1.1.3 eth1 (Ethernet 2nd adapter) eth1の(イーサネット第二アダプタ) 10 10
Router2 Router2の
Network IDネットワークID Network maskネットワークマスク Gatewayゲートウェイ Interface (examples; may vary)インターフェース(例;異なる場合があります) Cost (decreases the TTL )コスト(減少TTLを )
0.0.0.0 ( default route ) 0.0.0.0( デフォルトルート ) 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.1 10.1.1.1 eth0 (Ethernet 1st adapter) eth0の(イーサネットアダプタ第一) 10 10
172.16.1.0 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.1.1 172.16.1.1 eth1 (Ethernet 2nd adapter) eth1の(イーサネット第二アダプタ) 10 10
Router3 がrouter3
Network IDネットワークID Network maskネットワークマスク Gatewayゲートウェイ Interface (examples; may vary)インターフェース(例;異なる場合があります) Cost (decreases the TTL )コスト(減少TTLを )
0.0.0.0 ( default route ) 0.0.0.0( デフォルトルート ) 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.1 10.1.1.1 eth0 (Ethernet 1st adapter) eth0の(イーサネットアダプタ第一) 10 10
192.168.1.0 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.96 192.168.1.96 eth1 (Ethernet 2nd adapter) eth1の(イーサネット第二アダプタ) 10 10
Router2 manages its attached networks and default gateway; router 3 does the same; router 1 manages all routes within the internal networks. Router2は、接続されているネットワークとデフォルトゲートウェイを管理します。ルータ3は、同じ処理を行います。ルータ1は、内部ネットワーク内のすべてのルートを管理します。
Accessing internal resources If PC2 (172.16.1.100) needs to access PC3 (192.168.1.100), since PC2 has no route to 192.168.1.100 it will send packets for PC3 to its default gateway (router2). PC2は、そのデフォルトゲートウェイ(ルータ2)にPC3のパケットを送信します。192.168.1.100へのルートを持たないので、PC2(172.16.1.100)は、PC3(192.168.1.100)にアクセスする必要がある場合は、内部リソースへのアクセス 。 Router2 also has no route to PC3, and it will forward the packets to its default gateway (router1). Router2はまた、PC3へのルートを持たない、それはそのデフォルトゲートウェイ(ルータ1)にパケットを転送します。 Router1 has a route for this network (192.168.1.0/24) so router1 will forward the packets to router3, which will deliver the packets to PC3; reply packets will follow the same route to PC2. Router1はPC3にパケットを配信していると、router3にパケットを転送しますので、Router1は、このネットワークのためのルート(192.168.1.0/24)を持っています。応答パケットは、PC2に同じルートをたどります。
Accessing external resources If any of the computers try to access a webpage on the Internet, like http://en.wiki pedia.o rg/ , the destination will first be resolved to an IP address by using DNS -resolving. 外部リソースにアクセスするコンピュータのいずれかが好きで、インターネット上のウェブページにアクセスしようとした場合http:// en.wiki pedia.o rg/~~V 、宛先が最初に使用してIPアドレスに解決されるDNS解像します。 The IP-address could be 91.198.174.2. IPアドレスは91.198.174.2である可能性があります。 In this example, none of the internal routers know the route to that host, so they will forward the packet through router1's gateway or default route .この例では、内部のルータのいずれも、そのホストへのルートを知らないので、ルータ1のゲートウェイまたはを介してパケットを転送するデフォルトルート 。 Every router on the packet's way to the destination will check whether the packet's destination IP-address matches any known network routes.宛先へのパケットの道上のすべてのルータがパケットの宛先IPアドレスは、任意の既知のネットワークルートに一致するかどうかを確認します。 If a router finds a match, it will forward the packet through that route; if not, it will send the packet to its own default gateway.ルータが一致するものを見つけた場合、そのルートを経由してパケットを転送します。ない場合は、それ自身のデフォルトゲートウェイにパケットを送信します。 Each router encountered on the way will store the packet ID and where it came from so that it can pass the request back to previous sender.途中で遭遇した各ルータは、パケットのIDを格納し、それがそのようにどこから来た、それは戻って、以前の送信側に要求を渡すことができます。 The packet contains source and destination, not all router hops.パケットが送信元と宛先ではなく、すべてのルータホップが含まれています。 At last the packet will arrive back to router1, which will check for matching packet ID and route it accordingly through router2 or router3 or directly to PC1 (which was connected in the same network segment as router1).最後にパケットがRouter2のか、router3によって、または直接にPC1(ルータ1と同じネットワークセグメントに接続されたもの)を介してパケットIDと、それに応じてルートをマッチングするかどうかをチェックしますこれは、Router1に戻って到着します。
The packet doesn't return If router1 routing table does not have any route to 192.168.1.0/24, and PC3 tries to access a resource outside its own network, then the outgoing routing will work until the reply is fed back to router1.応答がルータ1にフィードバックされるまで、Router1のルーティングテーブルに192.168.1.0/24へのルートを持っていない場合、パケットが返されません 、とPC3は、独自のネットワーク外のリソースにアクセスしようとすると、発信ルーティングが動作します。 Since the route is unknown to router1, it will go to router1's default gateway, and never reach router3.ルートがRouter1に未知であるので、ルータ1のデフォルトゲートウェイに移動し、router3によって到達することはありません。 In the logs of the resource they will trace the request, but the requestor will never get any information.リソースのログに、彼らは要求をトレースしますが、要求側は任意の情報を得ることはありません。 The packet will die because the TTL -value decrease to less than 1 when it is travelling through the routers or the router will see that it has a private IP and discard it.ため、パケットが死んでしまうTTLそれがルータを通過されるか、またはルータがプライベートIPを持っていることを確認し、それを破棄するときに値が1未満に減少します。 This could be discovered by using Microsoft Windows utility Pathping , since you only can ping until that router which has no route or wrong route.これは、使用することによって発見することができ、Microsoft WindowsのユーティリティをPathpingはあなただけでなく、ルート、または間違ったルートを持っていませんそのルータまでpingを実行できるので、。 (Note that some routers will not reply to pinging.) (いくつかのルータがpingを実行に応答しないことに注意してください。)
[ edit ] See also [ 編集 ] も参照してください。 route (command) : generic command for displaying/configuring TCP/IP routing tables (including gateways) on both Windows and Unix -clone systems. ルート(コマンド) :両方でTCP / IPルーティングテーブル(ゲートウェイなど)を表示/設定するための汎用コマンドのWindowsとUnixのクローンシステム。